Organizations are rapidly shifting from Content Management Systems (CMS) to Digital Experience Platforms (DXP) in the race to provide true value for their customers. To plan for how your organization can continue to grow, it’s important to know the differences between the two and when to consider making the shift.
What is a CMS?
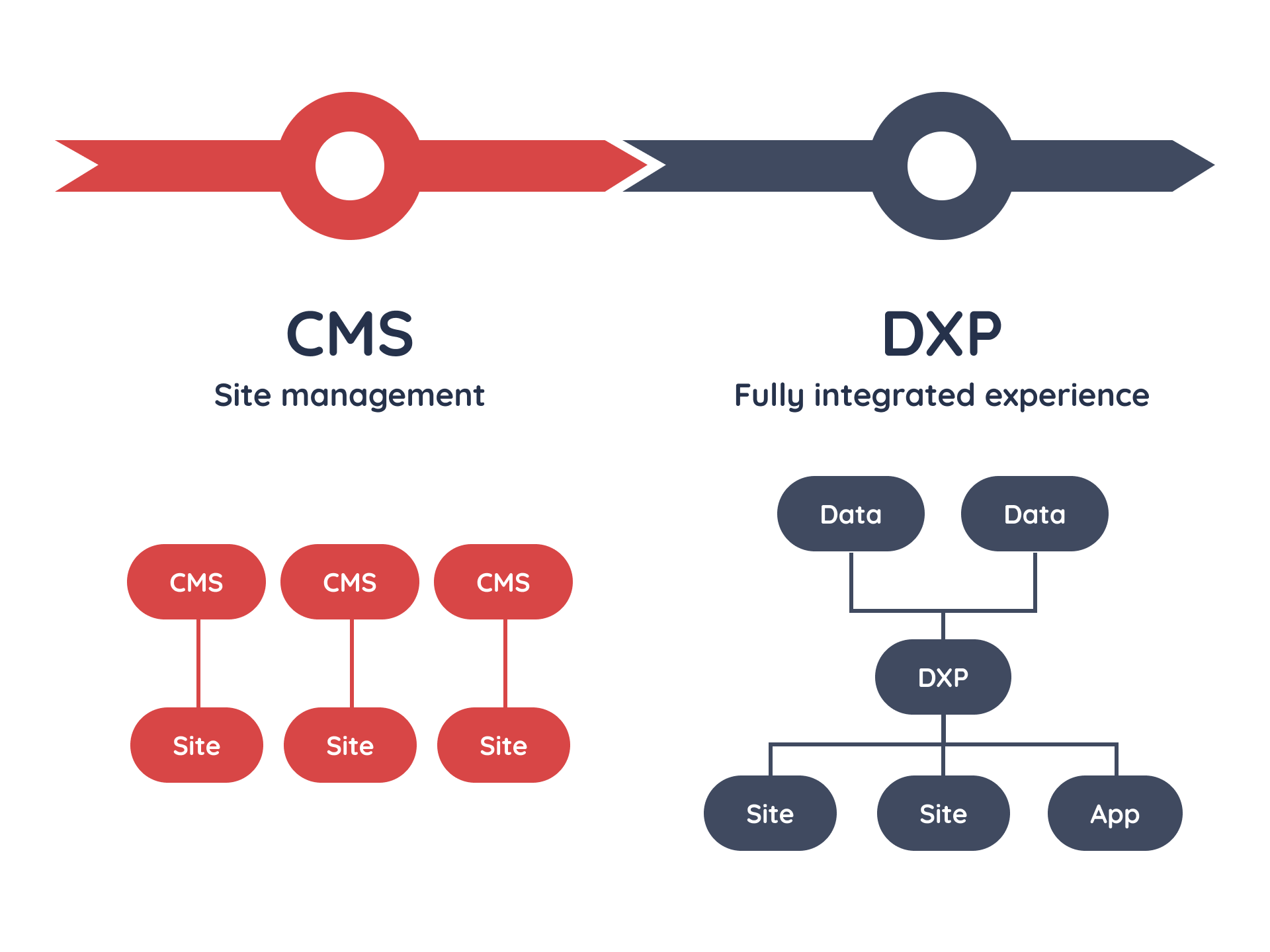
CMS have come a long way since then but, ultimately, the CMS was designed to publish content for users to read. Today, a CMS allows you to manage a website without having to code. The ability to easily build and manage websites using templates is a CMS’s biggest appeal, along with the ability to integrate various plug-ins, manage permissions for web management and schedule content ahead of time.
Core capabilities of a CMS
A CMS is organized around a set of core capabilities:
- Easy editing – CMSs have been built to offer no-code, drag-and-drop template solutions for marketers, designers and others to create and manage smooth digital experiences.
- Permissions – organizations can keep their content consistent and vet for compliance by creating custom permissions/checkpoints for content.
- Headless – headless CMS solutions allow you to publish and manage content across different endpoints from the one platform.
- Security – CMSs allow integrations with security solutions to protect users when interacting with your content, such as with forms.
- Analytics – integrate with analytics platforms to measure and act on user behaviors.
What is a DXP?
The Gartner definition of a DXP has been a popular example and one we often cite when explaining what a DXP is, and what it includes:
"A DXP is an integrated set of core technologies that support the composition, management, delivery and optimization of contextualized digital experiences. DXPs act as centers of gravity in a complex, extensive and interconnected technology landscape. Beyond simple websites and mobile apps, organizations need to deliver highly contextualized experiences to an increasing variety of modalities and channels across the customer journey."
In just a few years a lot has changed and DXPs aren’t just meeting the needs of marketers but linking up all areas of an organization. A DXP is not only about looking at the whole picture but also, it’s about listening to its users. DXPs have moved away from a strict headless CMS approach to give organizations the ability to orchestrate their entire customers’ digital experiences from one place.
Most importantly, DXPs reduce complexity for your business. They simplify and centralize processes, giving organizations the ability to orchestrate their entire customers’ digital experiences from one place, which leads to a range of benefits.
Core capabilities of a DXP
The core value of a DXP is its ability to tie up various systems together. This connectivity tends to plug gaps that otherwise might exist in a CMS, such as when trying to track user behavior and conversion opportunities.
Some of the most commonly utilized tools of a DXP include:
- Asset management – connect to your data and content sources directly from within your DXP.
- Personalization – showing more relevant content to different segments of users.
- Data storage – a secure way to store data that can be retrieved and shared across your system to support personalization.
- Search – DXPs support high-quality search on the front end as well as internally while offering ‘federated’ search results, i.e., those consolidated from various data repositories.
- Analytics – DXPs move from just delivering analytics to actually acting on them to support personalization and experience optimization - for example, customer journey mapping and A/B testing.
- Forms – DXPs allows you to utilize form data across a business, improving customer service and digitally transforming an organization.
CMS vs DXP: what’s the difference?
DXPs are often seen as an evolution from the CMS – offering the same core publishing capabilities but then enhancing an organization’s ability to interact with its users. Over time, DXPs have significantly differed from CMSs following the adoption of three major guiding principles.
Microservices
Microservices architecture involves an organizational and architectural approach to software development where individual services communicate across well-defined APIs and are managed by self-contained teams. This promotes greater flexibility (where services can be removed or added), faster rollout to market, and makes it easier to scale the development of applications.
In other words, there is less volatility in software development through DXPs due to the use of microservices. This contrasts with the famously siloed nature of CMSs within organizations, leading to risks such as unintentional insider threats/data breaches and sclerotic or chaotic decision-making.
Composable
DXPs have moved the market where businesses can now opt for plug-and-play business capabilities rather than limiting themselves to an all-in-one platform.
The functions of a DXP – from asset management and data storage through to analytics and automation – can operate as separate ‘packaged business capabilities’ (PBC). Yes, another acronym.
Similar in concept to microservices, this allows them to function independently while communicating through APIs. They are intended to be low-code solutions that are truly plug-in-and-play solutions for businesses.
MACH
DXPs build on the idea of headless CMSs, which is worth explaining.
A headless CMS ‘cuts the head off’ of the front end (what your users see) from the back end. This separates the presentation layer from the development layer. The advantage of a headless CMS is that it can store and deliver unified, structured content to multiple channels (i.e. apps, websites, emails, and IoT devices) all at once.
For example, a marketing team can easily roll out a temporary discount offer across website banners, apps, social media, paid advertising and email marketing.
MACH-based DXPs build on this idea and enhance your ability to interact with customers/users. MACH stands for ‘Microservices, API-first, Cloud-native and Headless’, meaning you can integrate external services (e.g., Salesforce or Google Analytics) into your management platform simply, without having to purchase a single all-in-one package. You also get the advantages of a headless CMS.
Benefits of a DXP over a CMS
All organizations need to find a solution to the exponential increase in business complexity that occurs as their business grows. DXPs are better designed than CMSs to support change and adaptability, which comes with a range of benefits.
Remove silos in your organization
DXPs are designed to surface the right data at the right time and to the right person; at the back end, this means connecting lots of different systems, centralizing business processes, and removing internal silos. The aim of all this is to provide a better customer experience (CX), but in doing so it also enables different teams to work together from one centralized platform.
DXPs make it possible to embrace the unknown
What your customers will want to do through digital touchpoints in the future is very difficult to predict, much less what those touchpoints will look like. A DXP provides both the agility and the flexibility your organization needs to be ready to not only respond to but lead these shifts.
Agility
Most modern, effective DXPs deliver experiences that offer a much faster time-to-value, meaning internal teams can spin up new sites, content, and services at speed. Whether this includes automation tools, templates, packaged integrations, or an intuitive UI – a DXP will enable your teams to create whatever your customers need, when they need it.
Flexibility
There are almost 10,000 different martech solutions in existence. Knowing which ones you’ll need in the next 3-5 years is as difficult as predicting customer expectations. Instead of gambling with your IT investments, select an open DXP that enables your organization to integrate best-of-breed solutions into your tech stack as and when needed.
For instance, Squiz Marketplace offers more than 40 secure integration connections to popular applications from vendors such as Microsoft, Salesforce, Google, Bitbucket, and more, without the need for custom code.
In addition, Squiz DXP Integrations provides generic connection components to integrate your Squiz DXP to any system that has an API, meaning even non-tech users can create new connections in minutes.
Make security the foundation of your organization
According to IBM, the average cost of a web security breach has risen to $4.35m USD – an increase of almost 12% in two years. How your website collects, stores, and uses customer data is under greater scrutiny than ever (as seen with Amazon’s hefty €746m fine in 2021, for breaking GDPR rules). Moreover, maintaining a high level of trust in your brand is still critical (trust remains second only to affordability in the customer decision-making process).
Designed to handle mass, complex data sets – and to create new sites and services at scale – most modern DXPs offer built-in tools to help audit and adhere to record-keeping and web standards.
Ultimately, DXPs protect organizations from insider risk, security risk, brand risk, and legal risk. By helping you to adhere to standards, like record keeping and accessibility, they act as a risk mitigation tool. Sometimes you move fast by grabbing a tool that solves something or lets someone build something and a DXP reduces the risk in doing so.
Stay on top of the increasing complexity
As customers conduct more of their day-to-day tasks online, across more devices and channels, the customer journey will become increasingly sophisticated and complex. If you’re already struggling to keep up with customer expectations, it’s definitely time to switch to a DXP.
CMSs were first built for web browsers, but increasingly web browsers are just a piece of the overall picture. And that's why we’ve seen the rise of the headless CMS.
All CMSs now need headless capability or they're not able to adapt to the modern world. But when people use headless CMSs they often comment on how much the head actually did for them. So you can very quickly find yourself in a position that's about your developers only, disempowering the rest of the organization and coming with associated development costs.
A DXP is about spanning both. It's about providing you with headless capabilities while retaining head-on capabilities and allowing you to operate through more channels.
Should you switch from a CMS to a DXP?
If you have complex needs as an organization that goes beyond simply publishing content, a DXP not only simplifies and centralizes your data sources, systems, and processes; its efficient pre-built components and templates can also cut valuable development time and lower business risk.
At a time when IT talent is at an all-time premium, creating a richer, more relevant customer experience shouldn’t require doubling your tech headcounts or adding to a sprawling, unmanageable IT ecosystem. Instead, switching your CMS to a DXP should be seen as a first positive step towards taking control of your organization’s digital transformation.
However, if you have a small business structure where you only need to publish content online with little interactivity for customer or data management, then sticking to a CMS for the time being is probably a safer (and cheaper!) choice.
The great thing with this option is that if you choose a CMS that comes as a feature of a wider DXP offering, you can integrate it later on into a DXP if your needs evolve.

